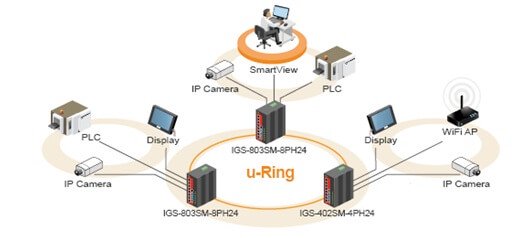
Redundancy is a crucial element of any industrial networks and applications. It protects industrial equipment and technological process from unexpected downtime and provides uninterrupted services for customers.
Nowadays, the proprietary u-Ring technology is highly recommended for industrial applications since it can achieve faster recovery time than any STP protocol.
What is u-Ring technology?
u-Ring is a proprietary redundancy technology that supports 250 units in a ring topology and can bring redundant paths into service within 10 ms when link failures occur. Compared with spanning tree protocol, u-Ring achieves faster recovery time on the network and is more flexible and scalable in network architecture.
So, u-Ring technology:
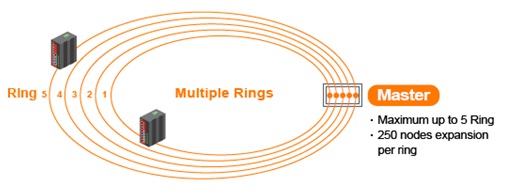
How u-Ring works?
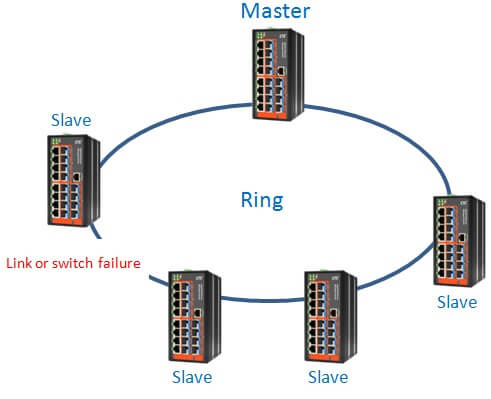
u-Ring redundancy technology automatically identifies the ring Master and then blocks one port in Master device for backup purposes. When the disconnection is detected on the network, u-Ring can bring backup ports back into “forwarding” mode, thus the disconnected segment can communicate with the whole network.
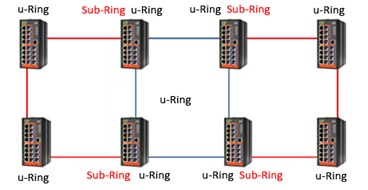
3 types of u-Ring Topologies
u-Ring supports 3 ring types:
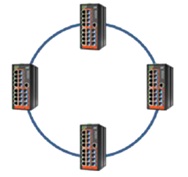
1. u-Ring type is used in a closed ring topology and all devices inside this ring must support u-Ring redundancy technology.
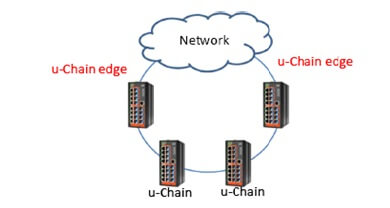
2. u-Chain type is used when u-Ring supported devices communicate with equipment or a network that do not support u-Ring redundancy technology.
3. Sub-Ring is used in an open ring and only has one node. In a networking topology, Sub-Ring type must co-exist with u-Ring type or u-Chain type. No third-party devices are used in this ring type.
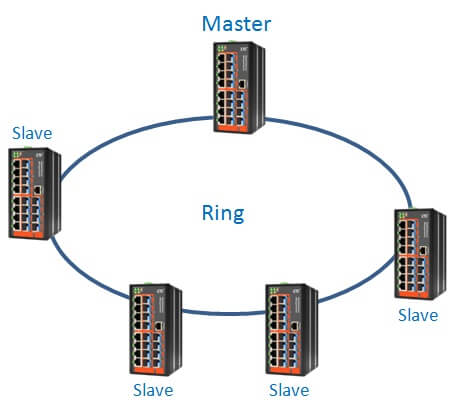
The algorithm of u-Ring redundancy technology (for u-Ring topology):
1. Definition of the “Master” device
The Master decides which segment will act as a backup path (however, the user-defined Master is also supported). If several devices are set or no device in a ring is set to Master, the u-Ring redundancy protocol assigns the device with the biggest MAC address the Master status.
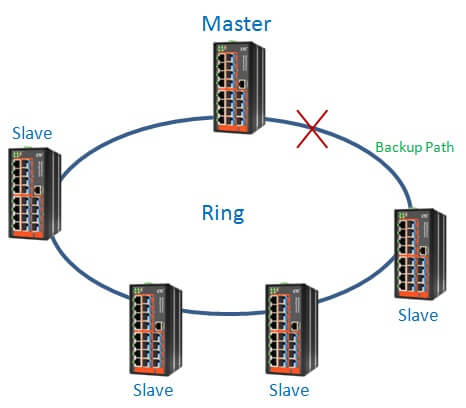
2. Blocking a port
The port with higher port number in Master device is blocked. The switch blocks backup port, and the transfer takes place on the main route.
3. Determination of link or switch failure
If physical link or connection in the ring is down, the status of backup path is changed from “blocked” to “forwarding”.
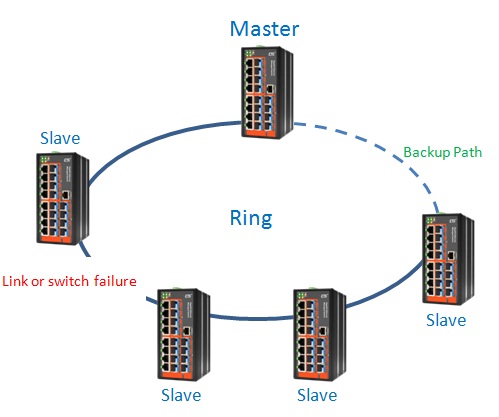
4. Switching to the backup path
The network works normally using redundant path.
Devices with u-Ring redundancy technology:
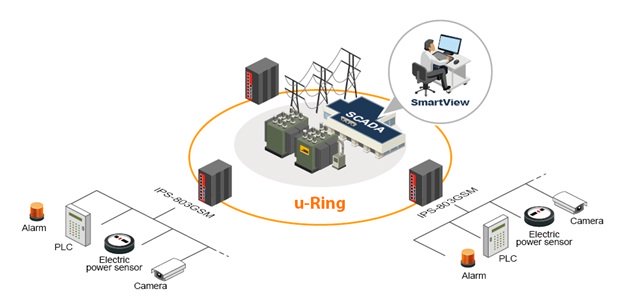
IPS-803/IPS-G803 Switches for Power Substations
These switches are designed to meet demands of substations and power stations and are fully compliant with IEC 61850-3 and IEEE 1613 requirements. Housed in rugged DIN rail or wall mountable enclosure with extended operating temperature range of -40°C to +85°C this switches are also suitable for any other harsh environments.
EN 50155 Managed FE Switches
This series of industrial switches are compliant with EN 50155 and EN50121-4 standards for Railway Traffic, providing stable and reliable Ethernet transmission. Reliable connections also are guaranteed by EMS, safety, freefall, shock and vibration certificates.
Industrial Managed Fast Ethernet and Gigabit switches
Having different combinations of Fiber and Copper Ethernet ports, Industrial Managed Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Switches are designed for harsh environments and industrial applicatons. They have a lot of certificates, such as FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class A, CE EN55022 Class A EMI and EMS certification which confirm better protection against unexpected lightning strikes, ESD or surges. Besides that they have EN50121-4 Railway Traffic, EN61000-6-2 and EN61000-6-4 Heavy Industrial Environment certificates, shock, freefall and vibration IEC60068-2-27, IEC60068-2-32, IEC60068-2-6 certificates. Some models supports SyncE and IEEE 1588 PTP v2 timing synchronization and also have wide (-40 to 75°C) operating temperature range.
Industrial Managed Fast Ethernet PoE and Gigabit PoE switches
In addition to robust industrial specifications, these models of Industrial Switches have several PoE ports and support advanced PoE management functions.