The aim of the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is to synchronize the time between different nodes inside Ethernet network.
This industrial protocol has several advantages compare to other synchronization technologies. First of all, IEEE 1588 PTP v2 protocol offers more timing accuracy needs for the applications than NTP and IRIGB protocols. Secondly, it’s very cost-effective, because one network needs just one GPS receiver to synchronize all devices in this network using IEEE 1588 PTP v2 protocol. Moreover, IEEE 1588 standard fulfils IEEE C37.118 Synchrophasor Data requirements, that’s why this standard is very famous in power generation and increasingly applied in substation to synchronize MU, IED and others protection devices.
The IEEE 1588 technology is not only applicable for power generation but for automation, telecommunications, robotics and other industries, because it defines a Precision Time Protocol and time-sensitive components for precise clocks synchronization in distributed systems. Futhermore, this protocol supports synchronization accuracy in the sub-microsecond range with minimal computing resources.
What Are the Key Advantages of Precision Time Protocol technology?
This synchronization technology provides sub-microsecond timing accuracy over standard Ethernet networks, far exceeding the precision of older protocols. It enables highly synchronized operations across multiple devices, reducing latency and ensuring perfect coordination in time-sensitive industrial processes.
Devices which supports IEEE 1588 PTP v2 protocol:
Industrial Core Switch
Supporting the huge amounts of routing protocols and having extended routing functionality, the industrial Core Switch or Backbone Switch is definitely the center of any network.
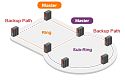
The Core Switch Switch fulfils a diversiityi of industrial-grade standards, providing a wide variety of redundant mechanisms and high density of Ethernet ports. This device supports u-Ring redundancy protocol that can establish 14 independent rings for flexible backbone infrastructures.
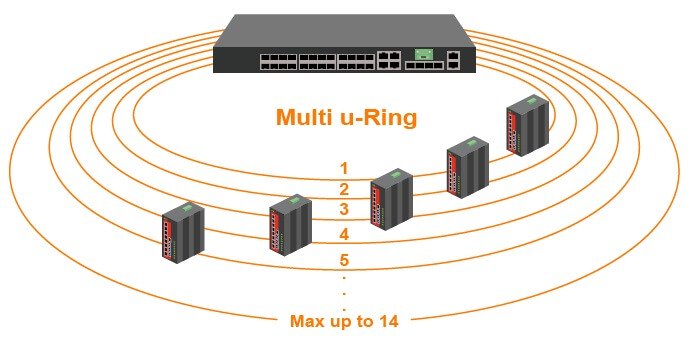
The Backbone Switch has the electromagnetic susceptibility certifications and is also certificated against shock-, freefall- and vibration influences. This future-proof up-to-date powerful switch should be considerate for building vital networks and is ideal for deployments in heavy industrial environment and railway traffic, especially at areas with very high or low temperatures.
What is IEEE 1588 synchronization and how does it function?
This technology functions by establishing a hierarchical clock structure where a master clock sends precise time stamps to various slave devices across a network. By calculating and compensating for transmission delays and hardware latency, it allows all connected components to maintain a unified and high-precision time base.
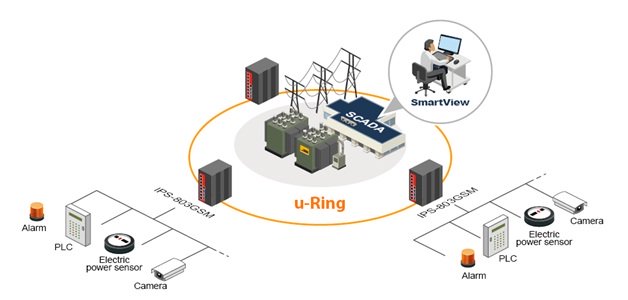
IPS-803/IPS-G803 Switches for Power Substations
These switches are designed to meet demands of substations and power stations and are fully compliant with IEC 61850-3 and IEEE 1613 requirements. Housed in rugged DIN rail or wall mountable enclosure with extended operating temperature range of -40°C to +85°C this switches are also suitable for any other harsh environments.
EN 50155 Managed FE Switches
This series of industrial switches are compliant with EN 50155 and EN50121-4 standards for Railway Traffic, providing stable and reliable Ethernet transmission. Reliable connections also are guaranteed by EMS, safety, freefall, shock and vibration certificates.

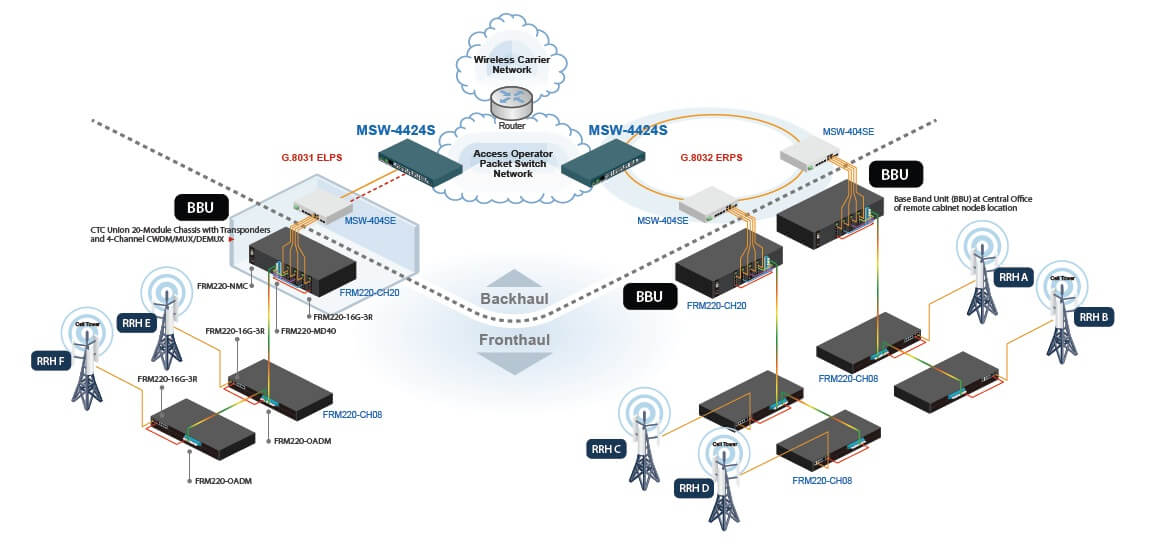
Carrier Gigabit Ethernet Switches
The MSW-4424CS and MSW-4424S managed Gigabit Ethernet switches are positioned as a Carrier Ethernet access switch solution and aimed specifically for Metro Ethernet deployment. The specifications of these switches are fully comply with the attributes of Carrier Ethernet proposed by the Metro Ethernet Forum.
Industrial Managed DIN-Rail Gigabit Ethernet Switches
Who needs this products, such as PTP-compliant networking hardware?
Engineers and operators in sectors like smart grid management, factory automation, and telecommunications require these solutions to ensure mission-critical synchronization. They are essential for any professional managing high-speed data acquisition systems where even minor time discrepancies can lead to system failures.
IGS-1608SM-SE, IGS-1608SM-SE-E, IGS-804SM-SE, IGS-804SM-SE-E models offers SyncE & IEEE 1588 PTP v2 timing synchronization features that allow to use this device in mobile backhaul application, providing optimal stability and reliability for services.
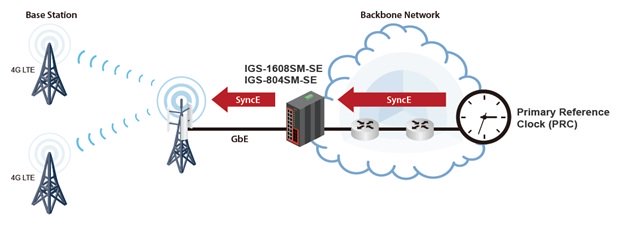
Supporting IEEE1588 PTP V2 for precise time synchronization, these models can operate in Ordinary-Boundary, Peer to Peer Transparent Clock, End to End Transparent Clock, Master, Slave mode by each port.
Furthermore, these Industrial Switches have EN50121-4 Railway Traffic, EN61000-6-2 and EN61000-6-4 Heavy Industrial Environment certificates, shock, freefall and vibration IEC60068-2-27, IEC60068-2-32, IEC60068-2-6 certificates.
RUGGEDCOM Devices
RUGGEDCOM products are well-known industrial communication devices which provide a high level of robustness and reliability in harsh environments. They are fully comply with IEC61850-3 standard and also provide a lot of other valuable features such as High Speed Redundancy Protocol (HRP), Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) etc.

How helps this products to achieve precise network coordination?
These synchronization tools eliminate the need for separate dedicated timing cables by delivering precision clock signals directly over existing Ethernet infrastructure. This integration simplifies system architecture while providing the high-level coordination necessary for complex robotic movements and distributed control systems.