Ethernet is the foundation of most modern networking environments. It powers everything from home networks to large data centers and has been instrumental in driving the growth of digital technologies over the last few decades. As businesses and homes demand higher speeds and more reliable connections, understanding Ethernet standards, cables, and speeds becomes crucial.
In this article, we explore the evolution of Ethernet technology, its different standards, types of cables, and speed capabilities, and provide technical examples to guide your choices.
What Are the Key Advantages of Ethernet Networking Solutions Like ICP DAS ET-2255U and Planet IGS-10020HPT?
Ethernet networking solutions from manufacturers such as ICP DAS ET-2255U and Planet IGS-10020HPT deliver high-speed, reliable connectivity and robust performance for industrial and enterprise applications. They improve network scalability and stability, ensuring efficient data transfer and future-proof infrastructure deployment.
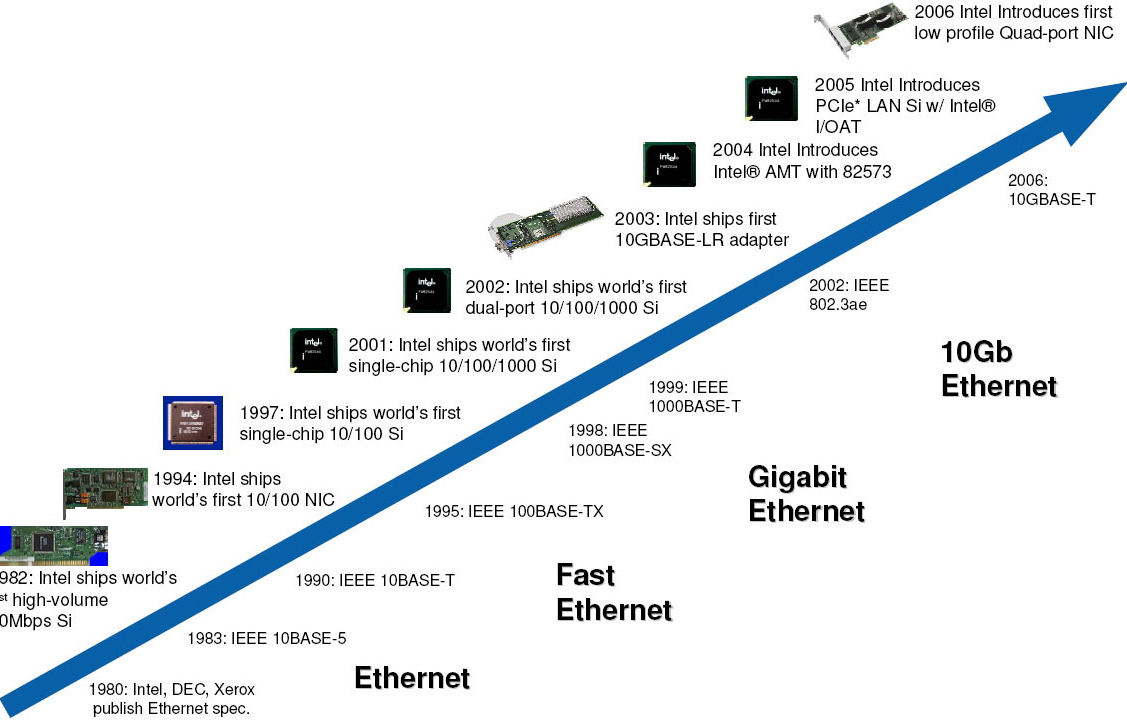
Key Versions and Their Evolution
Ethernet standards are defined by the IEEE 802.3 committee. These standards ensure compatibility and performance across different network environments. The most important revisions of Ethernet standards include:
What Are the Key Benefits of Industrial Ethernet I/O Modules Like the ICP DAS ET-2255U?
Industrial Ethernet I/O modules such as the ICP DAS ET-2255U provide flexible, high-performance networked input/output control with built-in Ethernet connectivity, simplifying installation and reducing wiring complexity. The ET-2255U supports standard protocols for seamless integration into automation systems and enhances reliability in industrial environments. :contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
1. IEEE 802.3: The Ethernet Standard
Ethernet has evolved in multiple stages, adapting to changing networking requirements. Some key versions include:
- 10BASE-T (Ethernet): The first Ethernet standard, supporting 10 Mbps speeds over twisted-pair copper cables. It revolutionized networking in the 1980s by enabling shared access to a common network.
- 100BASE-TX (Fast Ethernet): With speeds of 100 Mbps, Fast Ethernet became widely adopted in the late 1990s, replacing 10BASE-T. It was commonly used in small office networks for general internet use.
- 1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet): The next major leap, offering 1 Gbps speeds, was widely adopted in the early 2000s and has remained the standard for many office and home networks.
- 10GBASE-T (10 Gigabit Ethernet): This version supports speeds of up to 10 Gbps and is primarily used in high-demand environments like data centers and large enterprise networks.
- 40GBASE-T and 100GBASE-T: These ultra-fast Ethernet standards, supporting up to 100 Gbps, are mainly used in data centers and cloud computing infrastructure where massive data throughput is required.
Technical Example:

A large cloud provider may use 100GBASE-T Ethernet for interconnecting data centers, enabling fast data synchronization between multiple locations globally.
Ethernet Cable Types: Understanding the Different Categories
Ethernet cables are categorized into different types based on their performance characteristics, such as speed, distance, and shielding. These categories determine which networks and applications the cables can support.
1. Cat5e (Category 5 Enhanced)
- Maximum Speed: 1 Gbps
- Maximum Distance: 100 meters
- Cat5e cables are ideal for typical home networks, small offices, and light-duty tasks like web browsing and streaming HD content.
Technical Example:
A small office with a few users browsing the web and accessing files would benefit from Cat5e cables, as they provide sufficient speed for most office tasks.
2. Cat6 (Category 6)
- Maximum Speed: 10 Gbps (at shorter distances)
- Maximum Distance: 55 meters for 10 Gbps, 100 meters for 1 Gbps
- Cat6 cables are commonly used in business environments where more speed and performance are required, such as video conferencing or file sharing between workstations.
Technical Example:
In a medium-sized office with 20 employees, using Cat6 cables can ensure a fast and reliable network for tasks like large file transfers and real-time video meetings.
3. Cat6a (Category 6 Augmented)
- Maximum Speed 10 Gbps
- Maximum Distance: 100 meters
- Cat 6a cables are ideal for large office environments, data centers, and high-demand applications that require stable 10 Gbps speeds over longer distances.
Technical Example:
A data center with servers that need to handle 10 Gbps traffic between racks would use Cat6a cables for reliable and uninterrupted data transmission.
4. Cat7 (Category 7)
- Maximum Speed 10 Gbps
- Maximum Distance: 100 meters
- Cat7 cables provide superior shielding to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI). They are often used in environments with high levels of electrical interference, like industrial settings.
Technical Example:
In an industrial factory where machinery produces electrical noise, Cat7 cables can ensure a stable network connection without disruptions caused by interference.
5. Cat8 (Category 8)
- Maximum Speed 25 Gbps or 40 Gbps
- Maximum Distance: 30 meters
- Cat8 is designed for ultra-high-speed applications within data centers. It supports speeds up to 40 Gbps but is limited to short distances, typically used for connections within server racks.
Technical Example:
For a high-performance computing facility with short-distance connections between servers, Cat8 cables will provide maximum bandwidth for fast data processing and real-time data transfer.
Understanding Ethernet Speeds: What You Need to Know
Ethernet speed directly affects how quickly data can be transmitted across a network. The right speed depends on your network’s specific needs and applications.
1. Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps)
- Suitable for small home networks or offices with basic data needs, such as web browsing, email, and light media streaming.
-
Technical Example:
A home office with minimal devices, where the internet is used for browsing and sending emails, would benefit from 100 Mbps Ethernet.
2. Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps)
- The most common Ethernet speed for home and small office networks. Ideal for activities such as HD streaming, file sharing, and VoIP communications.
-
Technical Example:
In a household with multiple users streaming 4K videos and gaming online, Gigabit Ethernet is sufficient to handle the data requirements of the household.
3. 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps)
- Used in large enterprise environments, data centers, and high-demand applications like cloud storage, high-resolution video editing, and AI processing.
-
Technical Example:
A business running heavy workloads on virtualized machines across multiple servers will require 10 Gbps Ethernet to ensure smooth and fast communication between servers and users.
4. 40/100 Gigabit Ethernet
- These ultra-high-speed Ethernet standards are used in data centers and large-scale enterprise networks that require massive data throughput and minimal latency.
-
Technical Example:
A multinational corporation with numerous offices worldwide using real-time collaborative software and cloud computing will need 100 Gbps Ethernet for fast, global connectivity between their branches.
Choosing the Right Ethernet Cable for Your Network

Selecting the correct Ethernet cable is essential for achieving the desired performance. Consider the following when choosing cables:
- Cat5e or Cat6: Best for home networks or small offices with speed requirements up to 1 Gbps.
- Cat6a or Cat7: Suitable for larger office environments or data centers requiring 10 Gbps speeds with robust shielding against interference.
- Cat8: Ideal for high-performance data centers where ultra-high-speed connections between devices are necessary.
Who needs Industrial Ethernet Switches?
Reliable industrial switches are essential for large-scale enterprises and factories that require robust connectivity and power in harsh environments. For instance, Planet offers the IGS-10020HPT managed switch for high-power PoE requirements, while WoMaster provides the DS108H for secure DIN-rail installations in automation control cabinets. These devices ensure stable network performance where standard equipment might fail due to interference or extreme conditions.
Future-Proof Your Network with the Right Ethernet StandardsEthernet continues to evolve, offering faster speeds and more reliable connections for modern networking needs. By understanding Ethernet standards, cable types, and speed capabilities, you can ensure that your network supports both current and future applications.
Whether you're setting up a home network or managing a large-scale data center, choosing the right Ethernet solution will help you maintain a high-performing, scalable infrastructure.
Browse top networking products from leading manufacturers:
- ICP DAS – Industrial-grade Ethernet I/O systems and communication solutions
- Planet – Reliable Ethernet switches and media converters
- CTC UNION – Advanced fiber networking and industrial Ethernet equipment
- Nexcom – Ruggedized networking appliances and edge computing devices
- Leonton – Secure and intelligent industrial network switches
- WoMaster – Innovative Ethernet solutions for smart cities, railways, and automation
Recommended Products for Ethernet Networking

1. ICP DAS – Industrial Ethernet I/O Modules
- ET-2255U by ICP DAS | IPC2U: An Ethernet I/O module featuring an 8-channel wet/dry contact digital input and an 8-channel sink/source-type digital output. It includes a 2-port Ethernet switch for flexible networking.
- PET-7051 by ICP DAS | IPC2U: This module offers 16-channel isolated digital inputs and supports Power over Ethernet (PoE), simplifying installation in industrial environments.
2. Planet – Managed Ethernet Switches
- IGS-10020HPT by Planet | IPC2U: An industrial-grade, managed L2+ Ethernet switch with 8 Gigabit PoE ports and 2 Gigabit SFP slots. It supports IEEE 802.3at PoE+, delivering up to 30W per port, suitable for high-power devices.
- GS-2210-16P2S by Planet | IPC2U: A managed switch offering 16 Gigabit PoE+ ports and 2 Gigabit SFP ports. It's designed for enterprise networks requiring reliable PoE support and fiber connectivity.
3. CTC UNION – Industrial Ethernet Solutions
- GSW-3208MP by CTC Union | IPC2U: A managed Gigabit L2 PoE Ethernet switch with 8 PoE ports and 2 SFP ports. It supports 100-240VAC input power and operates within a 0...50°C temperature range, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
- IMC-1000C-E-SC001 by CTC Union | IPC2U: An industrial unmanaged Gigabit Ethernet media converter that converts 10/100/1000Base-T to 1000Base-X optical multi-mode SC port, supporting distances up to 500m.
4. Nexcom – Network Security Appliances
- NSA-3170A by NEXCOM | IPC2U: A 1U rackmount network communication appliance powered by the Intel® Xeon® processor E3-1200 v5/v6 family. It supports up to 32GB DDR4 memory and offers 8 copper LAN ports, suitable for high-performance networking tasks.
- NSA-1160 by NEXCOM | IPC2U: A compact network security appliance equipped with the Intel Atom® processor C3558, designed to provide a secure environment for network communication in small to medium enterprises.
5. Leonton – Industrial Ethernet Switches
- BG5-1204-SFP by Leonton | IPC2U: An industrial managed Gigabit Ethernet PoE++ switch with 8x10/100/1000Base-T PoE ports and 4x100/1000Base-X SFP ports. It features an IP30-rated metal enclosure, suitable for harsh industrial environments.
6. WoMaster – Industrial IoT Solutions
- DS108H by WoMaster | IPC2U: An 8-port industrial Ethernet switch designed with a robust housing for DIN-Rail installations in automation control cabinets, ensuring reliable network performance in harsh environments.
These products are designed to meet various networking requirements, from industrial automation to enterprise-level data centers.
Ready to Upgrade Your Network?
Looking to boost your network performance with reliable, high-quality Ethernet solutions? We’re here to help.
Get expert advice today!
Contact us for a free consultation and personalized recommendations tailored to your business or home setup.
How Network Security Appliances help to secure enterprise traffic
These devices allow businesses to manage high-performance data processing while ensuring a secure environment for critical communication. For example, NEXCOM manufactures the NSA-3170A, a powerful rackmount appliance designed for heavy networking workloads, and the compact NSA-1160 for protecting small to medium-sized enterprises. Deploying these specialized appliances helps organizations maintain robust network integrity and reliability.

