
Table of contents:
BACnet (Building Automation and Control network) is a network communication protocol for building automation and control networks that allows building automation systems or components from different manufacturers to exchange information and control functions.
BACnet was developed by the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Engineers ASHRAE, which led to the creation of the American standard ANSI/ASHRAE 135, and then the ISO 16484-5 standard.
BACnet device
A BACnet device consists of standard BIBB (BACnet Interoperability Building Block) function blocks that allow data to be exchanged between devices from different manufacturers. The BIBB block is a multilevel structured model consisting of several levels:
- BIBB
- Services
- Devices
- Objects
- Properties
The BIBBs for each BACnet device are listed in the PICS (Protocol Implementation Conformance Statement) document, which describes in detail the type of this BACnet device and its ability to interact with other devices.
BIBB
BIBB blocks (BACnet Interoperability Building Block) are subdivided into several functional interface areas (interoperability areas) that define application classes:
- Data sharing (DS)
- Alarm or event management (AE)
- Scheduling (SCHED)
- recording graphs of changes in values (T, Trending)
- Device (DM) and (NM) Network management
- Virual Terminal (VT)
- and others
Services
BACnet devices implement various services that perform communication and control functions. BACnet services have a client attribute (data request) - A and a server attribute (data provision) - B, for example, a property reader block for a DS-RP-A client device can be decoded as follows:
- DS is the interface area "Data exchange"
- RP is the ReadProperty property
- A is the recipient of the data
For example, a BIBB remote device control class might include the following services:
- Who-Is (device search)
- I-Am (device response)
- Who-Has (object search)
- I-Have (response of the device containing the object)
- DeviceCommunicationControl
- ConfirmedPrivateTransfer
- UnconfirmedPrivateTransfer
- ReinitializeDevice
- ConfirmedTextMessage
- UnconfirmedTextMessage
- TimeSynchronization (time synchronization)
Services can be specified for the BIBB object access class:
- CreateObject (create an object)
- DeleteObject (delete an object)
- ReadProperty (read property)
- ReadPropertyConditional (read property by condition)
- ReadPropertyMultiple (read a group of properties)
- WriteProperty (write property)
- WritePropertyMultiple (write property group)
- AddListElement (add element to list)
- RemoveListElement (remove an element from the list)
Device and objects
Each BACnet device consists of standard objects. Here are some of them:
- Analog input (AI)
- Analog output (AO)
- Analog value (AV)
- Binary input (BI)
- Binary output (BO)
- Binary Value (BV)
- Multi-State Input
- Multi-State Output
- Calendar
- Event Enrollment
- File
- Notification Class
- Group
- Loop
- Program
- Schedule
- Command
- Device
- HVAC (Heating Ventilating Air Conditioning)
- and others
Properties
Each BACnet object has some set of properties that describe its behavior or control how it works, such as: object identifier, object name and type.
Data link and physical layers of BACnet data transmission
It is possible to transmit the BACnet protocol through LAN (Local Area Network) networks, which are represented by various technologies of the channel and physical layers:
- ARCNET
- Ethernet
- BACnet/IP
- PTP (Point-To-Point) through RS-232
- MS/TP (Master-Slave/Token-Passing) through RS-485
- LonTalk
Examples of building a BACnet LAN network:

If BACnet devices use the same LAN environment for data transmission, then each device from any manufacturer can directly access another device. This type of LAN allows for direct device-to-device communication.

If BACnet devices use different LAN environments, then special gateway routers are used to combine them, which repackage BACnet messages in accordance with a certain standard of this BACnet network.

If devices with a different protocol and data transmission medium need to be connected to BACnet devices, then special protocol gateways are used. For devices to communicate over IP networks, the BACnet protocol provides 2 modes of operation: tunneling IP messages and using the BACnet/IP protocol.
BVLL concept for BACnet/IP
Addendum 135a to the BACnet protocol introduces the concept of BACnet Virtual Link Layer (BACnet Virtual Link Layer), which allows a BACnet/IP device to access the IP network infrastructure as if it were some kind of local LAN network. This type of connection is called a "virtual data link". It allows you to conveniently use various networks such as Ethernet, ATM, SONET, Frame Relay, ISDN and others.
Message transfer from device to BACnet/IP device occurs directly via an Ethernet local area network or the Internet. Broadcasting requires the use of a dedicated BACnet/IP Broadcast Management Device (BBMD). BBMD also provides registration of a device external to the BACnet network.
Examples of building a BACnet LAN network:
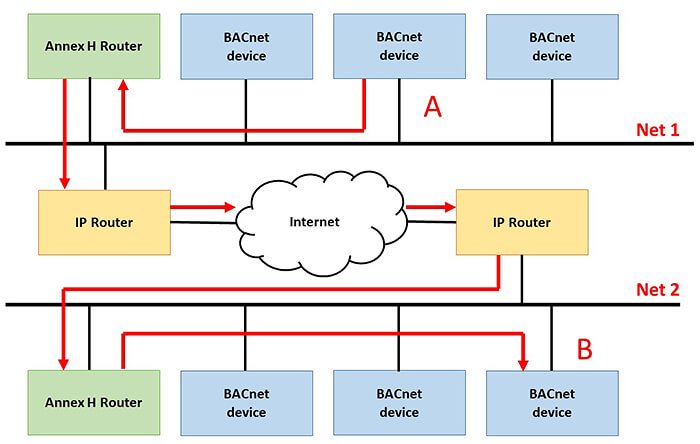
In BACnet IP tunneling mode, the device does not need to "understand" the IP protocol. Most of the work with the IP protocol is handled by a specialized router called the Annex H Router.

Devices with the BACnet/IP protocol are a full-fledged node of the IP network. They have their own IP address, support the IP protocol stack, and do all the work with the IP protocol themselves. Therefore, BACnet/IP devices transmit messages over the local network or the Internet directly without intermediaries.
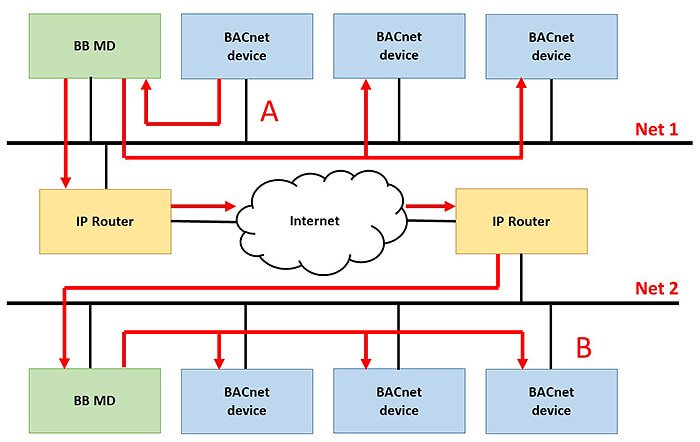
BACnet/IP broadcast data is handled through a dedicated BACnet/IP Broadcast Management Device (BBMD).
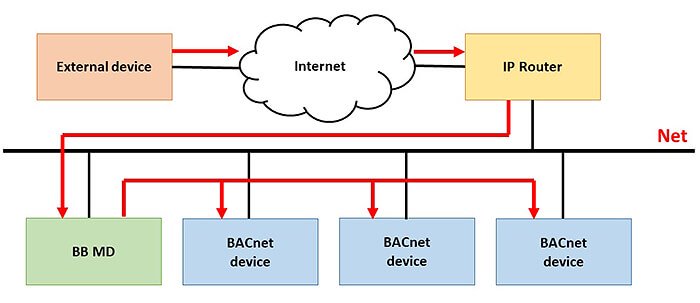
To connect an external device from the Internet to a BACnet network, use the BBMD device.
Connecting BACnet devices to APCS
There are many devices with BACnet protocol that solve various tasks for building automation, heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) control, lighting and access control, as well as ensuring the operation of fire detection systems and other devices. All of these devices are intended for solving problems inside the building, but usually they cannot be connected directly to industrial control systems and SCADA systems, or vice versa. To solve this problem, special protocol gateways are designed, which are presented below.

MGate 5217I-600-T - Modbus RTU/ASCII/TCP Master/Client to BACnet/IP Server gateway, max. 600 connections
MGate 5217I-1200-T - Modbus RTU/ASCII/TCP Master/Client to BACnet/IP Server gateway, max. 1200 connections
For further technical information, inquiries about offers or placement of orders, please contact our sales team at sales@ipc2u.com




