
We do know that an out-of-the-box managed switch can operate with no configurations, but ONLY as an unmanaged one. Hence, we are to configure a switch so that it can fulfill the required tasks.
Read also: What is the difference between managed and unmanaged switches?
Let’s consider the most widespread functions and their configuration using a web interface.
VLANs
The main function of managed switches is, obviously, dividing a core network into smaller subnets.
VLAN is a function that allows dividing a physical network into several virtual subnets, so that one subnet will correspond to a definite VLAN. For instance, sorting user computers by departments or positions (accounting, sales, logistics, etc.). Hence, networks with different VLAN will not be visible to each other. On the physical layer, the network remains untouched, meaning that several VLANs go through the same connection.
This increases security of each subnet. It is worth noting that, due to such division, the broadcast domain traffic is reduced (i.e. the data to be sent to all network participants).
The key point of VLAN configuration is to fill in a table with accurate data for each switch port:

There exist several port modes:
- Access – for connection to untagged/terminal devices, for instance, a PC
- Trunk – connection of multiple untagged/tagged devices and/or switches
- Hybrid – similar to a trunk port, but includes ability to assign tags that are to be removed from the packets
Redundancy
One more function that requires a managed switch is redundancy.
Please remember, that an unmanaged switch does NOT support ring topology.
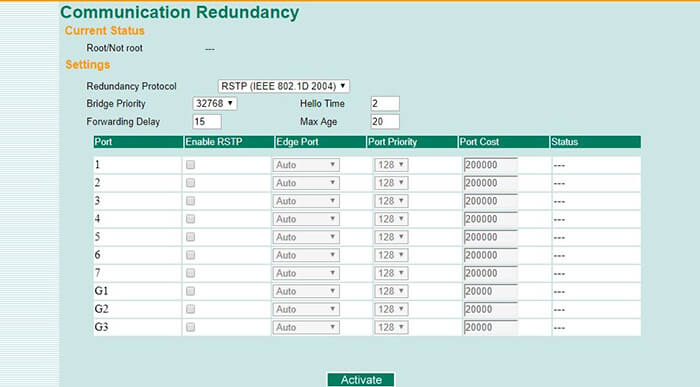
The most popular redundancy protocol is RSTP (Rapid spanning tree protocol).
To configure RSTP is much easier, than to understand the way it operates with port modes. So, let’s consider the general concept only:
You have a network of switches (group). You enable RSTP function on all switches and they form a tree topology themselves. You choose the root switch (Root). Other switches of the network search the shortest way to it. The paths that are not used any more become redundant.
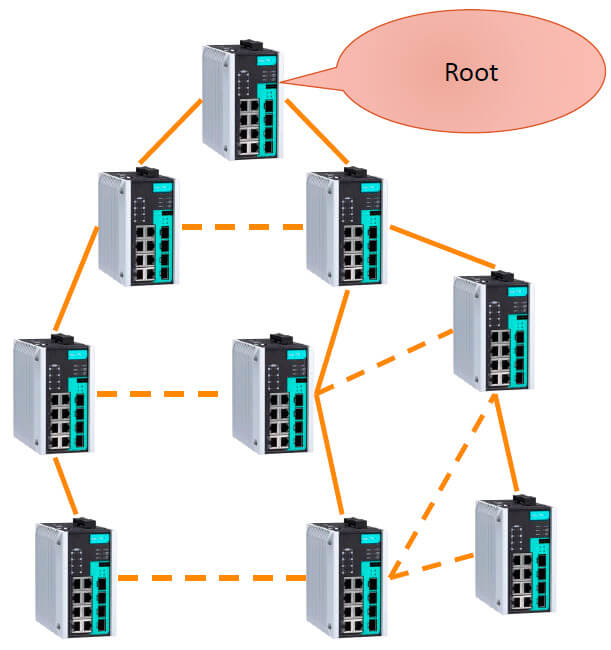
In the settings, there should be specified the switch ports, on which RSTP function must be enabled:
Turbo Ring & Turbo Chain
The modern redundancy protocols, such as Turbo Ring and Turbo Chain, that ensure network recovery time of under 20 ms, and their configuration have already been discussed previously.
Port Trunking
Port Trunking is an interesting function that helps to increase network throughput. The concept involves combining several physical channels into a single logical channel with performance equal to the sum of the links involved.
This also ensures redundancy (if one of the links fails, traffic will go through the others).
In the settings, there should be selected the ports that must be combined in trunk. Then the trunk group must be selected.

The latest update of Turbo Pack 3 firmware from MOXA includes support of consolidation of the whole trunk group into a virtual logical Turbo Ring port. It means that now you can start with creating Turbo Ring redundancy in grouped links.
Port Lock function provides additional network security, due to the ability to control the access to separate switch ports.
For configuration, deactivate the correspondent port in the Enable column:

Port Security
Another security function that restricts the access to a port is Port Security. It is done by assigning a MAC address to a definite port. Hence, the access to this port will be provided to a particular device only.
Configuration can be made in the form of a table:
Port = MAC address

Port Mirror
Port mirroring is applied to monitor data over a specific port by mirroring traffic from one port to another.
In the settings, there should be selected a port (monitored port) whose network activity will be monitored. Next, the watch direction must be selected (input traffic only, output traffic only or both). Then, there should be selected a port (mirror port) that will be used to monitor the network activity of the monitored port:

Monitoring
A managed switch has a microprocessor, hence, there is an opportunity to observe statistics in real time, for instance, real time tracking of the network resources status:

There exist monitoring of activity in total data transfer and that of activity of each separate port. It is also possible to select a type of packets:

Configuration restoration and firmware update
Once configuration of the device is done, there is always a chance that the settings can be accidentally reset, in case an unexperienced engineer makes troublesome changes. For such occasions, there is a tool (flash drive) ABC-02-USB that makes a backup of all switch configurations and can restore them. It can also update firmware. To do so, you need to connect a configurator to a switch and reset it. When starting, the switch will download all necessary configurations and/or update the firmware.

For further information and for the orders please contact our sales team sales@ipc2u.com

